

Thailand :: Geography
|
- The motorcycle taxis are unique to Thailand. They provide faster, albeit risker answer to the notorious traffic jams in Bangkok. Drivers wear a bright orange vest.
- The Tuk-Tuk or "Samlor" (motorized cabin cycle) offers another exciting means of transport in the city.
- Express boats ply the Chao Phraya River while canal boats ply the San sap canal.
At the famous Damnoen Saduak "Floating Market", boat-shops pack the narrow waterways selling all kinds of produce and food.
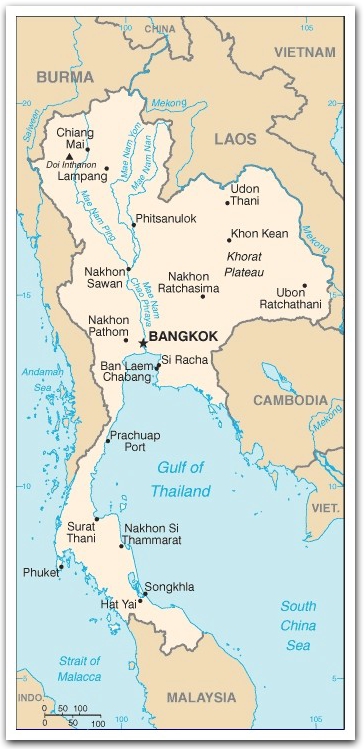
- shaped like an elephant's head ... the trunk is the south; the ear is the northeast; the mouth is the delta of the Chao Phraya River
- controls only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore
(land: 511,770 sq km; water: 2,230 sq km)
Terrain:
central plain (densely populated);
Khorat Plateau
mountains elsewhere
Elevation extremes
lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m;
highest point: Doi Inthanon
Major rivers: Chao Phraya (longest at 365 km), Mekong
The giant catfish, native to the Mekong River, is in danger of extinction due to overfishing, as well as decrease in water quality as a result of development and upstream damming. Fishing for the giant catfish is illegal in Thailand, Laos and Cambodia.Land use
arable land: 27.54%;
permanent crops: 6.93%;
other: 65.53% (2005)
Irrigated land: 49,860 sq km (2003)
Natural resources: tin, rubber, natural gas, tungsten, tantalum, timber, lead, fish, gypsum, lignite, fluorite, arable land
Climate: tropical monsoon;
mid-May to September: rainy, warm, cloudy southwest monsoon;
November to mid-March: dry, cool northeast monsoon;
southern isthmus always hot and humid
Natural hazards: land subsidence in Bangkok area resulting from the depletion of the water table; droughts
Environment issues: (1) air pollution from vehicle emissions; (2) water pollution from organic and factory wastes; (3) deforestation; (4) soil erosion; (5) wildlife populations threatened by illegal hunting