

Vietnam :: Geography
 Capital city: Hanoi
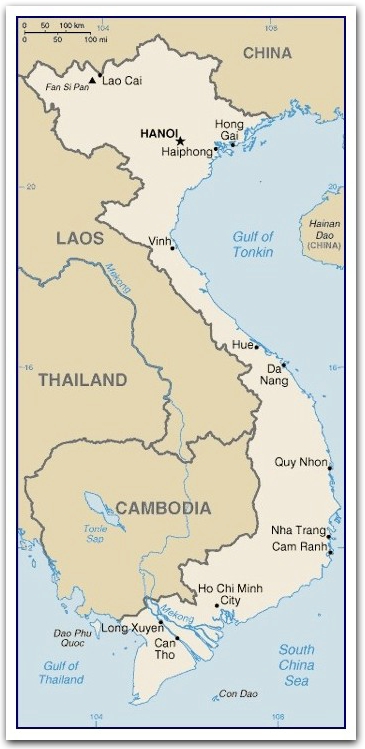
Capital city: HanoiLocation: Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Tonkin, and South China Sea, alongside China, Laos, and Cambodia ... shaped like an elongated letter "S".
Ha Long Bay in the Gulf of Tonkin was designated a World Heritage Site in 1994. The bay consists a cluster of 1,600 limestone monolithic islands with thick jungle vegetation and enormous caves.Area: 329,560 sq km; S-shaped
(land: 325,360 sq km; water: 4,200 sq km)
Terrain
low, flat delta in south and north;
central highlands;
hilly, mountainous in far north and northwest
Elevation extremes
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m;
highest point: Fan Si Pan
Land use
arable land: 20.14%;
permanent crops: 6.93%;
other: 72.93% (2005)
DeltasIrrigated land: 30,000 sq km (2003)
The rivers deposit rich soil to their deltas, making them ideal places for growing crops. Rice grown on the Mekong Delta produce almost half of Vietnam's total rice crop.
- Mekong Delta:
The Mekong River (4,184 km) is the longest river in Asia. It begins in Tibet; splits into nine smaller streams before flowing into the South China Sea near Ho Chi Minh City.
- Red River Delta: The Red River begins in China's Yunnan Province, flows through Vietnam before ending in the Gulf of Tonkin.

Natural resources: phosphates, coal, manganese, bauxite, chromate, offshore oil and gas deposits, forests, hydropower
Climate: tropical in south;
May to September: monsoonal in north with hot, rainy season;
October to March: warm, dry season
Natural hazards: occasional typhoons (May to January) with extensive flooding, especially in the Mekong River delta
Environment issues: (1) logging and slash-and-burn agricultural practices contribute to deforestation and soil degradation; (2) water pollution and overfishing threaten marine life populations; (3) groundwater contamination limits potable water supply; (4) growing urban industrialization and population migration are rapidly degrading environment in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City